襍ɩ侭荳玖スス
逎キ驟ク蛹茂ア蝙圽霑ɩーァ蛹夜ɩ豢サ蛹門「樒函蜿嶺ス捺蒲菴捺枚迪ョ蠑慕畑
髦ッサ⣨圽48 蜿大クɩ慮髣エ⣨ɩ019-8-19| 謠駱萓ﺚ蝠/th> | 荳頑オキ髮圽翠逕溽黄遘第橿譛蛾剞蜈ャ蜿ク | 襍ɩ侭螟ァ蟆/th> | 33.2KB |
|---|---|---|---|
| 襍ɩ侭蝗セ迚/th> | 荳玖スス谺。謨ー | 69谺。 | |
| 襍ɩ侭邀サ蝙/th> | PNG 蝗セ迚/i> | 豬剰ァ域ャ。謨ー | 548谺。 |
| 蜈崎エケ荳玖スス | 轤ケ蜃サ荳玖スス |
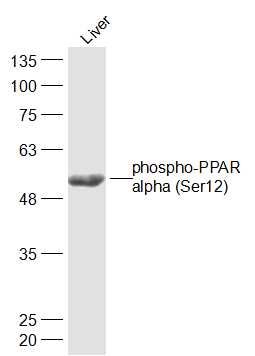
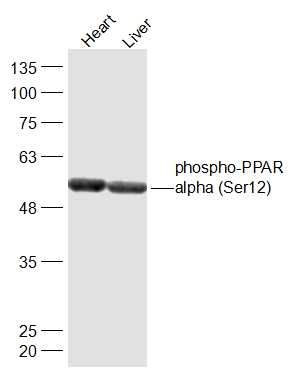
闍ア譁圽錐遘ーphospho-PPAR alpha (Ser12)
荳ュ譁圽錐遘ー逎キ驟ク蛹ɩalpha;蝙圽霑ɩーァ蛹夜ɩ豢サ蛹門「樒函蜿嶺ス捺蒲菴直br />蛻ォ 蜷恒PAR alpha (phospho-Ser12); PPAR alpha (phospho-S12); p-PPAR alpha (Ser12); p-PPAR alpha (S12); hPPAR; MGC2237; MGC2452; NR1C1; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 1; Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor alpha; PPAR; PPAR alpha; PPARA; OTTHUMP00000197740; OTTHUMP00000197741; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PPAR-alpha; PPARA_HUMAN; PPARalpha.
隸エ 譏荵ヲ100ul
莠ァ蜩∫アサ蝙狗」キ驟ク蛹匁蒲菴ɩnbsp;
遐皮ゥカ鬚圽沺閧ソ逖、 扈ɩ逕溽黄 蜈咲稔蟄ヲ 霓ャ蠖戊ー鰍蝗蟄ɩnbsp; 豼驟カ蜥檎」キ驟ク驟カ
謚嶺ス捺擂貅審abbit
蜈矩嚀邀サ蝙輝olyclonal
莠、蜿牙渚蠎禰uman, Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, Horse, Guinea Pig,
莠ァ蜩∝コ皮畑WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:400-800 IHC-F=1:400-800 IF=1:100-500 ⣨育浹陷。蛻・援髴蛛壽蒲蜴滉ソョ螟搾シɩnbsp;
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
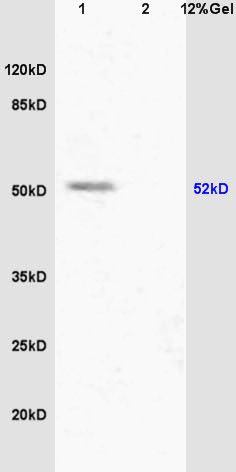
蛻蟄駱驥圽2kDa
扈ɩ螳壻ス咲サɩ譬ク
諤ァ 迥カLyophilized or Liquid
豬ɩnbsp; 蠎ヲ1mg/ml
蜈逍ォ 蜴檪LH conjugated Synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human PPAR alpha around the phosphorylation site of ser12:PL(p-S)PL
莠ɩnbsp; 蝙紀gG
郤ッ蛹匁婿豕病ffinity purified by Protein A
蛯ィ 蟄ﴚ豸イ0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
菫晏ュ俶擅莉カStore at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
PubMedPubMed
莠ァ蜩∽サ狗サ甲ackground:
Peroxisome proliferators are nongenotoxic carcinogens which are purported to exert their effect on cells through their interaction with members of the nuclear hormone receptor family, termed Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors (PPARs). Nuclear hormone receptors are ligand dependent intracellular proteins that stimulate transcription of specific genes by binding to specific DNA sequences following activation by the appropriate ligand. Studies indicate that PPARs are activated by peroxisome proliferators such as clofibric acid, nafenopin, and WY-14,643, as well as by some fatty acids. It has also been shown that PPARs can induce transcription of acyl coenzyme A oxidase and cytochrome P450 A6 (CYP450 A6) through interaction with specific response elements. PPAR alpha is activated by free fatty acids including linoleic, arachidonic, and oleic acids. Induction of peroxisomes by this mechanism leads to a reduction in blood triglyceride levels. PPAR alpha is expressed mainly in skeletal muscle, heart, liver, and kidney and is thought to regulate many genes involved in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids. Activation of rat liver PPAR alpha has been shown to suppress hepatocyte apoptosis. PPAR alpha, like several other nuclear hormone receptors, heterodimerizes with retinoic X receptor (RXR) alpha to form a transcriptionally competent complex.
Function:
Ligand-activated transcription factor. Key regulator of lipid metabolism. Activated by the endogenous ligand 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine (16:0/18:1-GPC). Activated by oleylethanolamide, a naturally occurring lipid that regulates satiety (By similarity). Receptor for peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Regulates the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Functions as transcription activator for the ACOX1 and P450 genes. Transactivation activity requires heterodimerization with RXRA and is antagonized by NR2C2.
Subunit:
Heterodimer; with RXRA. This heterodimerization is required for DNA binding and transactivation activity. Interacts with AKAP13, LPIN1 and PRDM16. Also interacts with PPARBP coactivator in vitro. Interacts with CITED2; the interaction stimulates its transcriptional activity (By similarity). Interacts with NCOA3 and NCOA6 coactivators. Interacts with ASXL1 AND ASXL2.
Subcellular Location:
Nucleus.
Tissue Specificity:
Skeletal muscle, liver, heart and kidney.
Similarity:
Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily.
Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain.
SWISS:
Q07869
Gene ID:
5465
Database links:
Entrez Gene: 5465 Human
Entrez Gene: 19013 Mouse
Entrez Gene: 25747 Rat
Omim: 170998 Human
SwissProt: Q07869 Human
SwissProt: Q6I9S0 Human
SwissProt: P23204 Mouse
SwissProt: Q542P9 Mouse
SwissProt: P37230 Rat
Unigene: 103110 Human
Unigene: 710044 Human
Unigene: 212789 Mouse
Unigene: 9753 Rat
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or di
| 莠ァ蜩∝崟迚/td> |
Sample:
Sample:
Sample:
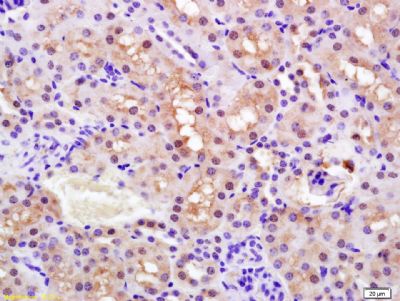
Tissue/cell: rat kidney tissue; 4% Paraformaldehyde-fixed and paraffin-embedded;
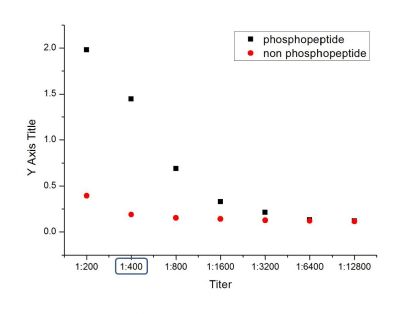
phosphopeptide non phosphopeptide |
 蛹門キ・莉ェ蝎ィ鄂令/a>
蛹門キ・莉ェ蝎ィ鄂令/a>